来源为:LeetCode图解算法数据结构
图书整理 I
书店店员有一张链表形式的书单,每个节点代表一本书,节点中的值表示书的编号。为更方便整理书架,店员需要将书单倒过来排列,就可以从最后一本书开始整理,逐一将书放回到书架上。请倒序返回这个书单链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,6,4,1]
输出:[1,4,6,3]
提示:
0 <= 链表长度 <= 10000
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
public int[] reverseBookList(ListNode head) {
List<Integer> li = new ArrayList<>();
ListNode tem = head;
while(tem != null){
li.add(tem.val);
tem = tem.next;
}
// if (li.isEmpty()) return null; // 处理空链表的情况
// ListNode ans = new ListNode(li.get(li.size() - 1));
// for(int i = li.size() - 2; i >= 0; i--){
// ListNode ne = new ListNode(li.get(i));
// ne.next = ans;
// ans = ne;
// }
// return ans;
for(int i = 0; i < li.size() / 2; i++){
Collections.swap(li, i, li.size() - i - 1);
}
int[] arr = li.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
return arr;
}
}
改进:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
public int[] reverseBookList(ListNode head) {
//count计数,倒序即可
int count = 0;
ListNode tem = head;
while(tem != null){
count++;
tem = tem.next;
}
int[] arr = new int[count];
tem = head;
while(tem != null){
arr[--count] = tem.val;
tem = tem.next;
}
return arr;
}
}
删除链表节点
给定单向链表的头指针和一个要删除的节点的值,定义一个函数删除该节点。
返回删除后的链表的头节点。
示例 1:
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], val = 5
输出: [4,1,9]
解释: 给定你链表中值为 5 的第二个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9.
示例 2:输入: head = [4,5,1,9], val = 1
输出: [4,5,9]
解释: 给定你链表中值为 1 的第三个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 5 -> 9.
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode tem = new ListNode();
tem = head;
//找到第一个看有么有,没有直接不彳亍
while(head != null){
if(head.val != val){
tem.val = head.val;
head = head.next;
break;
}
head = head.next;
}
ListNode ans = tem;
//有了头部新建就好
while(head != null){
if(head.val != val){
ListNode li = new ListNode(head.val);
tem.next = li;
tem = li;
}
head = head.next;
}
return ans;
}
}
更新:
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
//哑节点
dummy.next = head;
ListNode prev = dummy;
while (prev.next != null) {
if (prev.next.val == val) {
prev.next = prev.next.next; // 跳过当前节点
} else { //注意这里的else,极端情况下出现空指针。
prev = prev.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
链表倒置
开辟新空间
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public ListNode trainningPlan(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return head;
}
List<Integer> l = new ArrayList<>();
ListNode l1 = head;
while(l1 != null){
l.add(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
}
ListNode ansHead = new ListNode();
ListNode ans = ansHead;
for(int i = l.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--){
ListNode tem = new ListNode();
tem.val = l.get(i);
ansHead.next = tem;
ansHead = tem;
}
return ans.next;
}
}
原地倒置
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public ListNode trainningPlan(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return head;
}
ListNode pre = null;//是最终的,在最末尾,左部
ListNode tem = null;//用于中途放置head的下一个
while(head != null){
tem = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = tem;
}
return pre;
}
}
链表倒数第i个节点获取
给定一个头节点为 head 的链表用于记录一系列核心肌群训练项目编号,请查找并返回倒数第 cnt 个训练项目编号。
示例 1:
输入:head = [2,4,7,8], cnt = 1
输出:8
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public ListNode trainingPlan(ListNode head, int cnt) {
int count = 0;
ListNode tem = head;
while(tem != null){
count++;
tem = tem.next;
}
tem = head;
for(int i = count; i != cnt; i--){
tem = tem.next;
}
return tem;
}
}
上面是先遍历一遍,再去找到相应位置的。还可以采用双指针的方式来做,中间相差了cnt个数,快的指针到了null,也就是low到倒数第cnt个。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public ListNode trainingPlan(ListNode head, int cnt) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode low = head;
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++){
fast = fast.next;
}
while(fast != null){
fast = fast.next;
low = low.next;
}
return low;
}
}
链表合并
给定两个以 有序链表 形式记录的训练计划 l1、l2,分别记录了两套核心肌群训练项目编号,请合并这两个训练计划,按训练项目编号 升序 记录于链表并返回。
注意:新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:输入:l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]
示例 3:输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode trainningPlan(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode anshead = new ListNode();
ListNode ans = anshead;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null){
if(l1.val >= l2.val){
ListNode li = new ListNode();
li.val = l2.val;
l2 = l2.next;
anshead.next = li;
anshead = anshead.next;
}else{
ListNode li = new ListNode();
li.val = l1.val;
l1 = l1.next;
anshead.next = li;
anshead = anshead.next;
}
}
while(l1 != null){
ListNode li = new ListNode();
li.val = l1.val;
l1 = l1.next;
anshead.next = li;
anshead = anshead.next;
}
while(l2 != null){
ListNode li = new ListNode();
li.val = l2.val;
l2 = l2.next;
anshead.next = li;
anshead = anshead.next;
}
return ans.next;
}
}
当然这道题没说得重新开内存,直接赋值l1,l2就好了,这么写内存开销大了就。
链表相交
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
解释:第一个正式训练项目编号为 8 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
int len1 = 0, len2 = 0;
ListNode tem1 = headA;
ListNode tem2 = headB;
while(tem1!= null){
len1++;
tem1 = tem1.next;
}
while(tem2!= null){
len2++;
tem2= tem2.next;
}
tem1 = headA;
tem2 = headB;
if(len1 >= len2){
for(int i = 1; i <= len1 - len2; i++){
tem1 = tem1.next;
}
}else{
for(int i = 1; i <= len2 - len1; i++){
tem2 = tem2.next;
}
}
while(tem1 != null){
if(tem1.val == tem2.val){
return tem1;
}else{
tem1=tem1.next;tem2=tem2.next;
}
}
return null;
}
}
上述解法找到两个差了长度多少,长的先找,短的等到长的与其长度一样的时候在一起向后走,直到相遇或者null。
但还是下面这种更巧妙。

public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode A = headA, B = headB;
while (A != B) {
A = A != null ? A.next : headB;
B = B != null ? B.next : headA;
}
return A;
}
}
泪目了。
链表复制
请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
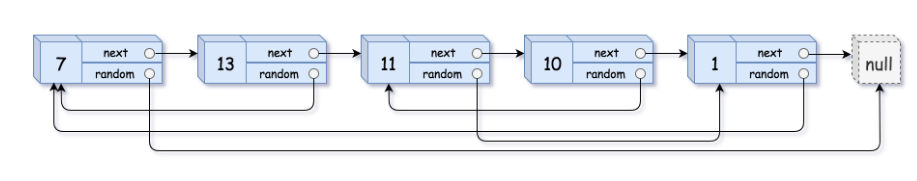
==是把内存地址重新开辟==
简单思路,先来直接新的next节点,进行连接。后续每次O(n)查找相应对应位置的信息,遍历啊。
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
Node dummy = new Node(0);
Node li = dummy;
Node tem = head;
while(tem != null){
Node tem1 = new Node(tem.val);
tem1.next = tem.next;
li.next = tem1;
li = li.next;
tem = tem.next;
}
tem = head;
li = dummy.next;
while(tem != null){
if(tem.random != null){
Node nodeyuan = head;
Node nodehou = dummy.next;
while(nodeyuan != tem.random){
nodeyuan = nodeyuan.next;
nodehou = nodehou.next;
}
li.random = nodehou;
}
tem = tem.next;
li = li.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
优化的话,每次查询之前的random新的节点,使用Map
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null){
return null;
}
Node cur = head;
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<Node, Node>();
while(cur != null){
map.put(cur, new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
}