图书整理
读者来到图书馆排队借还书,图书管理员使用两个书车来完成整理借还书的任务。书车中的书从下往上叠加存放,图书管理员每次只能拿取书车顶部的书。排队的读者会有两种操作:
push(bookID):把借阅的书籍还到图书馆。
pop():从图书馆中借出书籍。
为了保持图书的顺序,图书管理员每次取出供读者借阅的书籍是 最早 归还到图书馆的书籍。你需要返回 每次读者借出书的值 。
如果没有归还的书可以取出,返回 -1 。
示例 1:
输入:
[“BookQueue”, “push”, “push”, “pop”]
[[], [1], [2], []]
输出:[null,null,null,1]
解释:
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1]
myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue)
myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2]
==简单的队列操作==
import java.util.*;
class CQueue {
Queue<Integer> queue;
public CQueue() {
queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
public void appendTail(int value) {
queue.offer(value);
}
public int deleteHead() {
if(!queue.isEmpty()){
int res = queue.peek();
queue.poll();
return res;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
}
/**
* Your CQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* CQueue obj = new CQueue();
* obj.appendTail(value);
* int param_2 = obj.deleteHead();
*/
最小栈
请你设计一个 最小栈 。它提供 push ,pop ,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
实现 MinStack 类:
MinStack() 初始化堆栈对象。
void push(int val) 将元素val推入堆栈。
void pop() 删除堆栈顶部的元素。
int top() 获取堆栈顶部的元素。
int getMin() 获取堆栈中的最小元素。

==采用两个栈,其中一个存储所有的数字,另一个按照越向栈顶数字越小的方式形成==
因为在栈中,对于栈上部的操作是不会影响下面的数字的
class MinStack {
public Stack<Integer> s1;
public Stack<Integer> s2;
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MinStack() {
s1 = new Stack<Integer>();
s2 = new Stack<Integer>();
}
public void push(int x) {
s1.push(x);
if(s2.empty() || s2.peek() >= x){
s2.push(x);
}
}
public void pop() {
if(s1.peek().equals(s2.peek())){
s2.pop();
}
s1.pop();
}
public int top() {
return s1.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return s2.peek();
}
}
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack obj = new MinStack();
* obj.push(x);
* obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* int param_4 = obj.getMin();
*/
验证图书取出顺序
现在图书馆有一堆图书需要放入书架,并且图书馆的书架是一种特殊的数据结构,只能按照 一定 的顺序 放入 和 拿取 书籍。
给定一个表示图书放入顺序的整数序列 putIn,请判断序列 takeOut 是否为按照正确的顺序拿取书籍的操作序列。你可以假设放入书架的所有书籍编号都不相同。

==直接模拟栈即可==
class Solution {
public boolean validateBookSequences(int[] putIn, int[] takeOut) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
int index = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < takeOut.length; i++){
if(stack.empty()){
if(index != putIn.length){
stack.push(putIn[index++]);
}else {return false;}
}
if(stack.peek().equals(takeOut[i])){
stack.pop();
}else{
if(index != putIn.length){
stack.push(putIn[index++]);
}else return 1 == 0;
i--;
}
}
return true;
}
}
望远镜中最高海拔
科技馆内有一台虚拟观景望远镜,它可以用来观测特定纬度地区的地形情况。该纬度的海拔数据记于数组 heights ,其中 heights[i] 表示对应位置的海拔高度。请找出并返回望远镜视野范围 limit 内,可以观测到的最高海拔值。

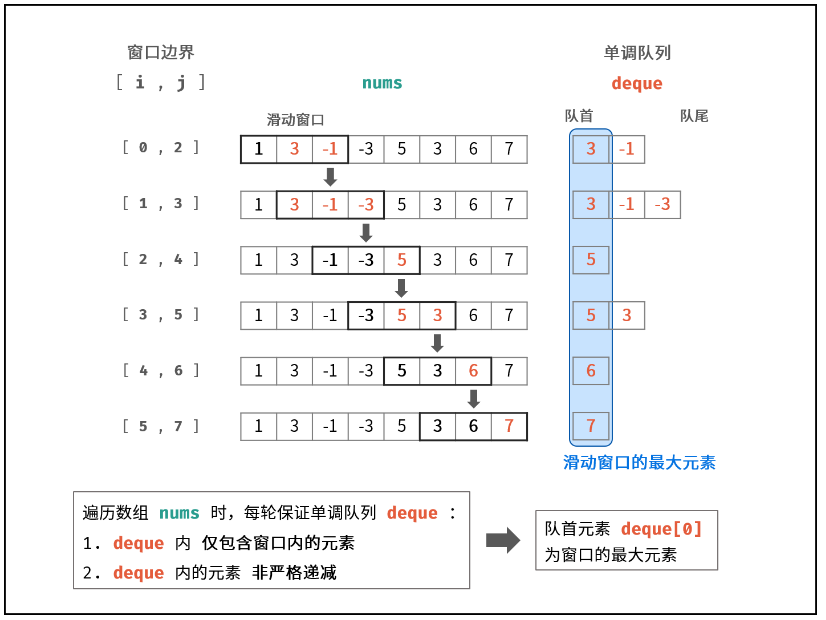
单调队列内每次仅仅有队首(所需要的最大值),队列后所存储的是以后可能作为最大值出现的值。维护这个单调队列即可。
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
class Solution {
public int[] maxAltitude(int[] heights, int limit) {
Deque<Integer> d = new ArrayDeque<>();
int heightLen = heights.length;
if(heightLen == 0) return new int []{};
int [] ans = new int[heightLen - limit + 1];
//滑动窗口形成之前
for(int i = 0; i < limit; i++){
while(!d.isEmpty() && heights[i] > d.peekLast()){
d.removeLast();
}
d.addLast(heights[i]);
}
ans[0] = d.peekFirst();
int j = 1;
//滑动窗口形成之后
for(int i = limit; i < heightLen; i++){
//判断是否需要移除已经不在滑动窗口之内的元素
if(d.peekFirst() == heights[i-limit]) d.removeFirst();
while(!d.isEmpty() && heights[i] > d.peekLast()){
d.removeLast();
}
d.addLast(heights[i]);
ans[j++] = d.peekFirst();
}
return ans;
}
}
设计自助结算系统
请设计一个自助结账系统,该系统需要通过一个队列来模拟顾客通过购物车的结算过程,需要实现的功能有:
get_max():获取结算商品中的最高价格,如果队列为空,则返回 -1
add(value):将价格为 value 的商品加入待结算商品队列的尾部
remove():移除第一个待结算的商品价格,如果队列为空,则返回 -1
注意,为保证该系统运转高效性,以上函数的均摊时间复杂度均为 O(1)
==与上一题有异曲同工之妙,不过这里并没有窗口大小的限制,改成了出队的调用时间控制窗口==

import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Checkout {
public Deque<Integer> d = new ArrayDeque<>();
public Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
public Checkout() {
}
public int get_max() {
if(d.isEmpty()) return -1;
return d.peekFirst();
}
public void add(int value) {
q.add(value);
while(!d.isEmpty() && value > d.peekLast()){
d.removeLast();
}
d.addLast(value);
}
public int remove() {
if(q.isEmpty()) return -1;
int res = q.peek();
q.remove();
if(res == d.peekFirst()){
d.removeFirst();
}
return res;
}
}
/**
* Your Checkout object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Checkout obj = new Checkout();
* int param_1 = obj.get_max();
* obj.add(value);
* int param_3 = obj.remove();
*/
数据流中的中位数
中位数 是有序整数列表中的中间值。如果列表的大小是偶数,则没有中间值,中位数是两个中间值的平均值。
例如,
[2,3,4] 的中位数是 3
[2,3] 的中位数是 (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5
设计一个支持以下两种操作的数据结构:
void addNum(int num) - 从数据流中添加一个整数到数据结构中。
double findMedian() - 返回目前所有元素的中位数。
==大根堆与小根堆==

import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class MedianFinder {
//小根堆,这里存储大的数字
PriorityQueue<Integer> p1 = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> (x - y));
//大根堆,这里存储小的数字
PriorityQueue<Integer> p2 = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> (y - x));
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MedianFinder() {
}
public void addNum(int num) {
if(p1.size() == p2.size()){
p2.add(num);
p1.add(p2.poll());
}
else{
p1.add(num);
p2.add(p1.poll());
}
}
public double findMedian() {
if(p1.size() == p2.size()){
return (double)(p1.peek() + p2.peek()) / 2.0;
}else{
return p1.peek();
}
}
}
/**
* Your MedianFinder object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MedianFinder obj = new MedianFinder();
* obj.addNum(num);
* double param_2 = obj.findMedian();
*/