彩灯装饰记录 I
一棵圣诞树记作根节点为 root 的二叉树,节点值为该位置装饰彩灯的颜色编号。请按照从 左 到 右 的顺序返回每一层彩灯编号。
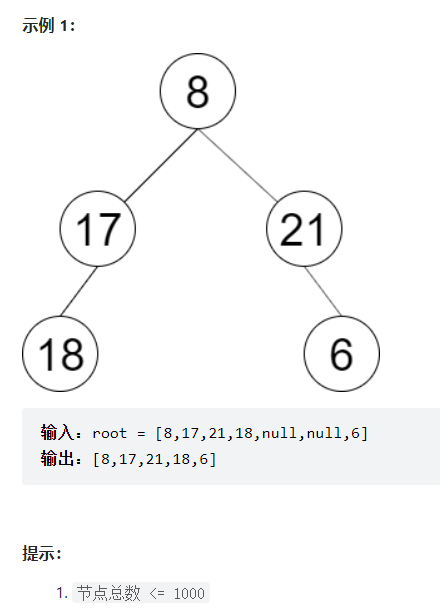
==其实说是最基础的BFS==
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
Queue<TreeNode> q;
Queue<Integer> q1;
int size = 0;
public int[] decorateRecord(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return new int[]{};
q = new LinkedList<>();
q1 = new LinkedList<>();
// TreeNode tem = root;
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
TreeNode tem = q.poll();
q1.offer(tem.val);
if(tem.left != null){
q.offer(tem.left);
}
if(tem.right != null){
q.offer(tem.right);
}
}
int[] res = new int[q1.size()];
int i = 0;
while(!q1.isEmpty()){
res[i++] = q1.poll();
}
return res;
}
// public int i = 0;
// public int[] res;
// public int quantity(TreeNode treeNode){
// if(treeNode == null){
// return 0;
// }else{
// return 1 + quantity(treeNode.left) + quantity(treeNode.right);
// }
//
// }
//
// public void traversal(TreeNode treeNode){
// if(treeNode == null){
// return;
// }
// res[i++] = treeNode.val;
// traversal(treeNode.left);
// traversal(treeNode.right);
// }
// public int[] decorateRecord(TreeNode root) {
// int len = quantity(root);
// res = new int[len];
// traversal(root);
// return res;
// }
}
class Solution {
public int[] decorateRecord(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return new int[0];
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(){{ add(root); }};
ArrayList<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
ans.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
}
int[] res = new int[ans.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++)
res[i] = ans.get(i);
return res;
}
}
彩灯装饰记录 II
一棵圣诞树记作根节点为 root 的二叉树,节点值为该位置装饰彩灯的颜色编号。请按照从左到右的顺序返回每一层彩灯编号,每一层的结果记录于一行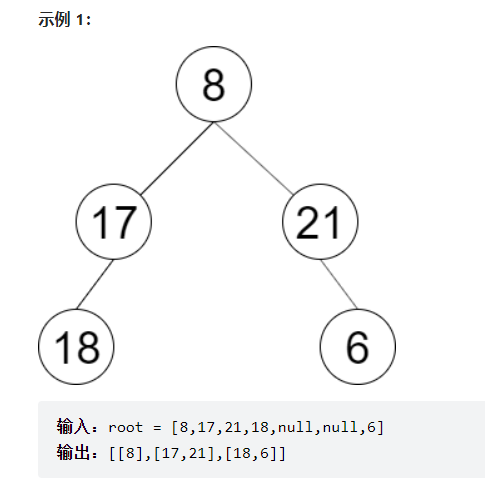
==思路还是bfs,每次遍历一层,做统计,中间写的有些冗余了==
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Solution {
private class Node{
int val;
public Node(int val, int ceng) {
this.val = val;
this.ceng = ceng;
}
int ceng;
}
public List<List<Integer>> decorateRecord(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Node> l = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
int layer = 0;
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
int len = q.size();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
TreeNode tem = q.poll();
// e node = new Node(tem.val, layer);
arr.add(tem.val);
if(tem.left != null){
q.offer(tem.left);
}
if(tem.right != null){
q.offer(tem.right);
}
}
res.add(arr);
//layer++;
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> decorateRecord(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root != null) queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = queue.size(); i > 0; i--) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
tmp.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
}
res.add(tmp);
}
return res;
}
}
作者:Krahets
链接:https://leetcode.cn/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/lhch2t/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
彩灯装饰记录 III
一棵圣诞树记作根节点为 root 的二叉树,节点值为该位置装饰彩灯的颜色编号。请按照如下规则记录彩灯装饰结果:
第一层按照从左到右的顺序记录
除第一层外每一层的记录顺序均与上一层相反。即第一层为从左到右,第二层为从右到左。
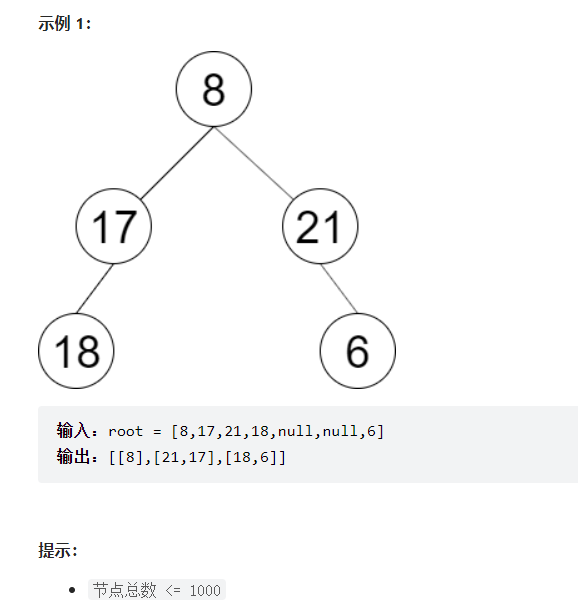
==bfs同时,判断该层是否需要翻转,采用Collections工具类==
==或使用Deque双端队列,List都可以前后插入==
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> decorateRecord(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
boolean reverse = false;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
int len = q.size();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
TreeNode tem = q.poll();
arr.add(tem.val);
if(tem.left != null){
q.offer(tem.left);
}
if(tem.right != null){
q.offer(tem.right);
}
}
if(reverse){
Collections.reverse(arr);
}
reverse = !reverse;
res.add(arr);
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> decorateRecord(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root != null) queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
LinkedList<Integer> tmp = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = queue.size(); i > 0; i--) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(res.size() % 2 == 0) tmp.addLast(node.val);
else tmp.addFirst(node.val);
if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
}
res.add(tmp);
}
return res;
}
}
作者:Krahets
链接:https://leetcode.cn/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/lhcbar/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
翻转二叉树
给定一棵二叉树的根节点 root,请左右翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
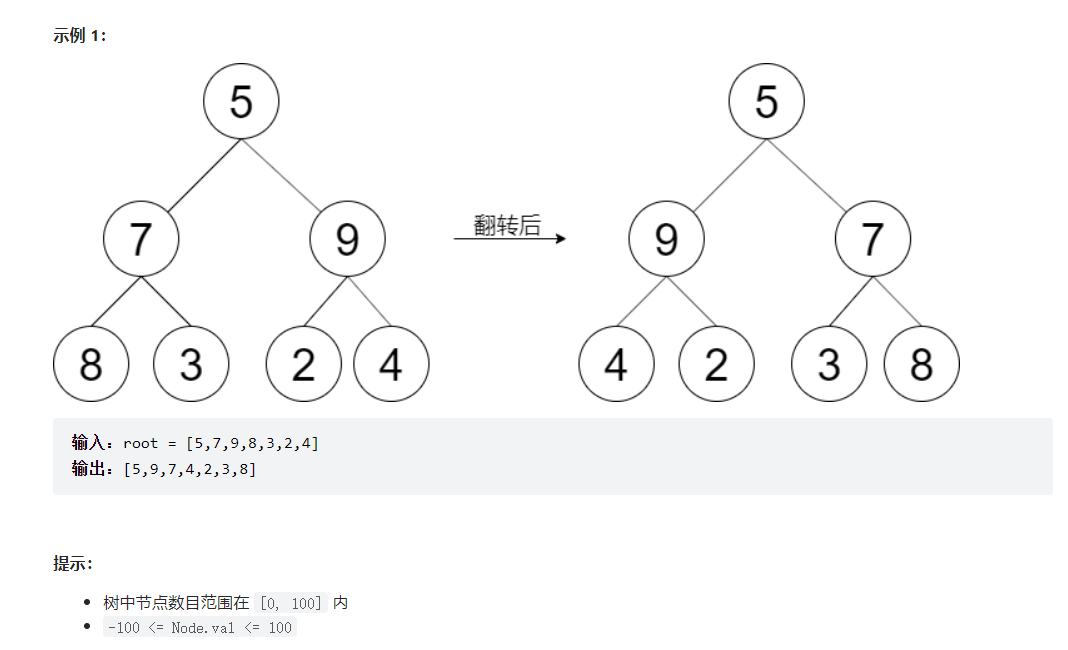
==直接交换左右子孩子==
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return null;
if(root != null) {
TreeNode tem = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tem;
}
if(root.left != null)
mirrorTree(root.left);
if(root.right != null)
mirrorTree(root.right);
return root;
}
}
判断对称二叉树
请设计一个函数判断一棵二叉树是否 轴对称 。
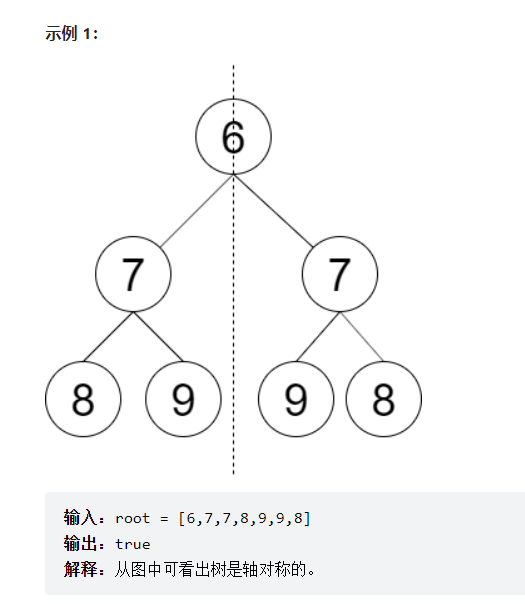
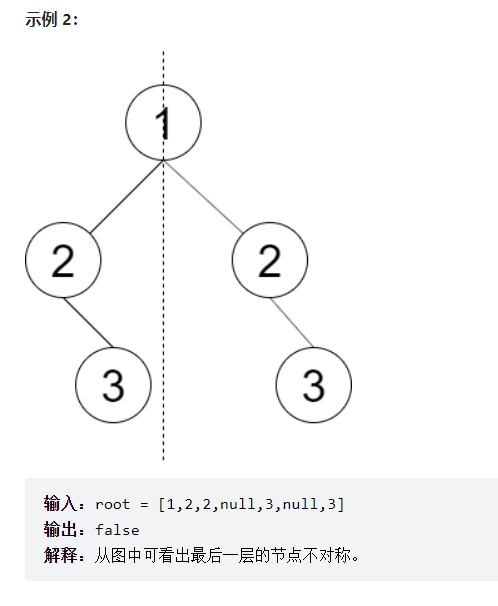
==思路:把左边第一个子孩子给反转了==
==另一个直接比较子孩子(4个),左边的和右边的比,巧妙啊==
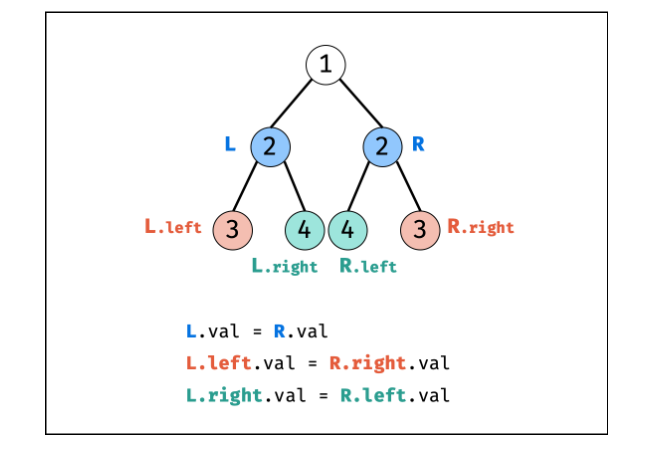
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void reverse(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return;
TreeNode tem = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tem;
reverse(root.left);
reverse(root.right);
}
public boolean isSame(TreeNode a, TreeNode b){
if(a == null ^ b == null){
return false;
}
if(a == null) return true;
if(a.val != b.val) return false;
return isSame(a.left, b.left) && isSame(a.right, b.right);
}
public boolean checkSymmetricTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return true;
if(root.left != null) reverse(root.left);
return isSame(root.left, root.right);
}
}
class Solution {
public boolean checkSymmetricTree(TreeNode root) {
return root == null || recur(root.left, root.right);
}
boolean recur(TreeNode L, TreeNode R) {
if(L == null && R == null) return true;
if(L == null || R == null || L.val != R.val) return false;
return recur(L.left, R.right) && recur(L.right, R.left);
}
}
作者:Krahets
链接:https://leetcode.cn/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/lhf6oh/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
将二叉搜索树转化为排序的双向链表
将一个 二叉搜索树 就地转化为一个 已排序的双向循环链表 。
对于双向循环列表,你可以将左右孩子指针作为双向循环链表的前驱和后继指针,第一个节点的前驱是最后一个节点,最后一个节点的后继是第一个节点。
特别地,我们希望可以 就地 完成转换操作。当转化完成以后,树中节点的左指针需要指向前驱,树中节点的右指针需要指向后继。还需要返回链表中最小元素的指针。
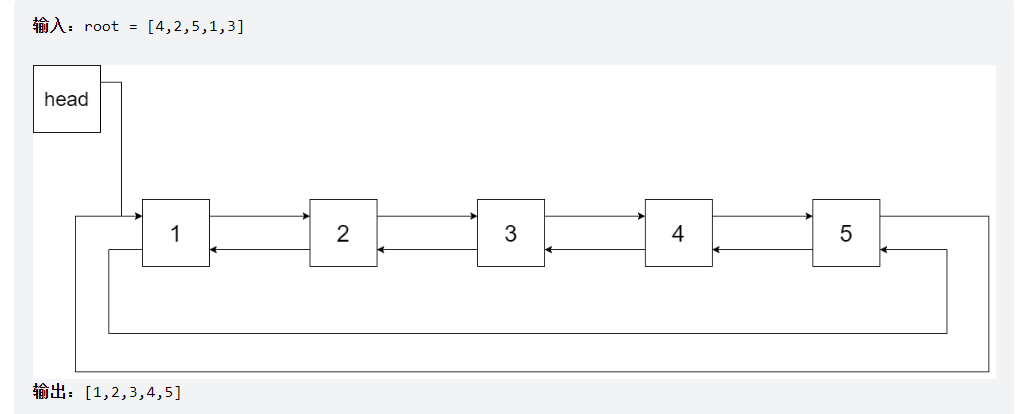
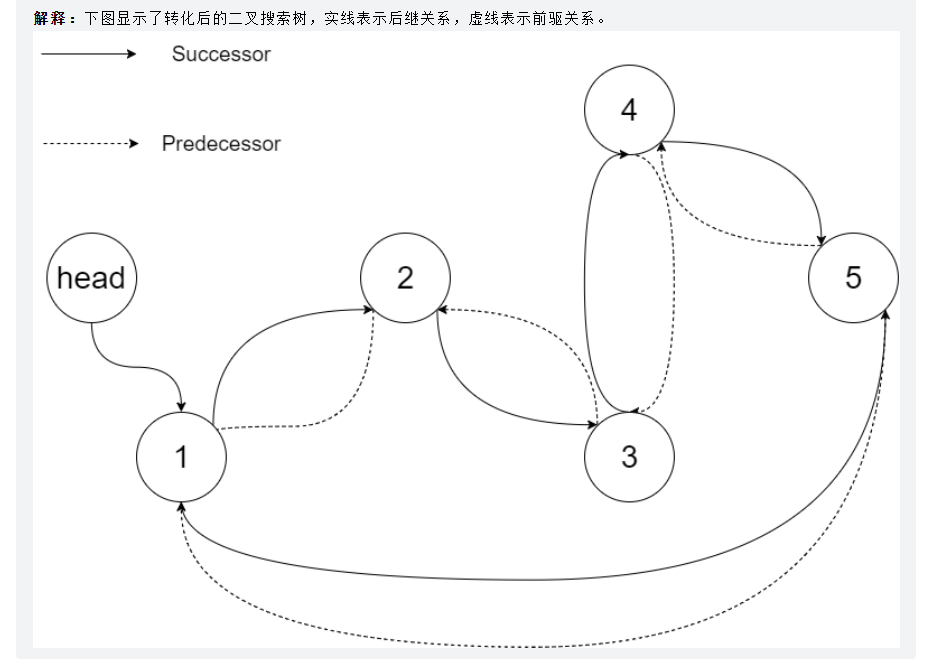
==中序遍历建立新的双向链表==
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val,Node _left,Node _right) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public Node dummy;
public Node i;
public void goNode(Node root){
if(root == null) return;
goNode(root.left);
Node node = new Node(root.val);
node.left = i;
i.right = node;
i = node;
goNode(root.right);
}
public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {
if(root == null) return null;
dummy = new Node();
i = dummy;
goNode(root);
dummy = dummy.right;
i.right = dummy;
dummy.left = i;
return dummy;
}
}
class Solution {
Node pre, head;
public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {
if(root == null) return null;
dfs(root);
head.left = pre;
pre.right = head;
return head;
}
void dfs(Node cur) {
if(cur == null) return;
dfs(cur.left);
if(pre != null) pre.right = cur;
else head = cur;
cur.left = pre;
pre = cur;
dfs(cur.right);
}
}
作者:Krahets
链接:https://leetcode.cn/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/lxh893/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
寻找二叉搜索树中的目标节点
某公司组织架构以二叉搜索树形式记录,节点值为处于该职位的员工编号。请返回第 cnt 大的员工编号。
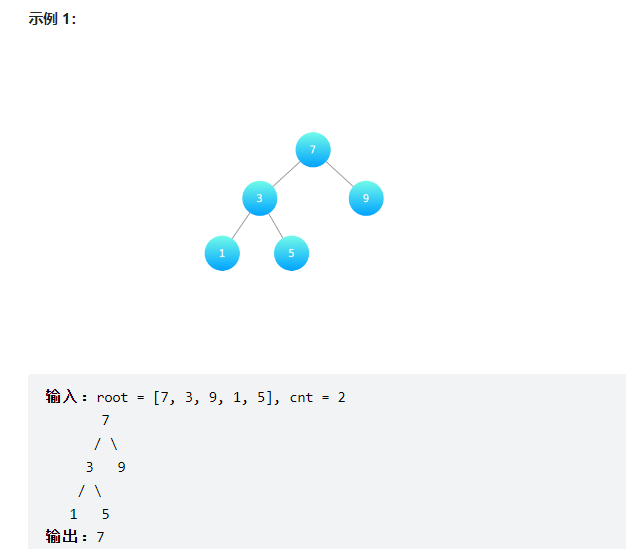
==中序遍历有n个,找n-cnt+1个==
==倒着中序遍历,直接可以找到相应的大小的位置(wtf)==
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int i = 1;
int sum = 0;
int ans = 0;
public void goTreeNode(TreeNode root, int cnt){
if(root == null) return;
goTreeNode(root.left, cnt);
if(i == sum - cnt + 1){
ans = root.val;
}
i++;
goTreeNode(root.right, cnt);
}
public void getSum(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return;
getSum(root.left);
sum++;
getSum(root.right);
}
public int findTargetNode(TreeNode root, int cnt) {
if(root == null) return -1;
getSum(root);
goTreeNode(root, cnt);
return ans;
}
}
class Solution {
int res, cnt;
public int findTargetNode(TreeNode root, int cnt) {
this.cnt = cnt;
dfs(root);
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return;
dfs(root.right);
if(cnt == 0) return;
if(--cnt == 0) res = root.val;
dfs(root.left);
}
}
作者:Krahets
链接:https://leetcode.cn/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/lxxi5m/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
计算二叉树的深度
某公司架构以二叉树形式记录,请返回该公司的层级数。
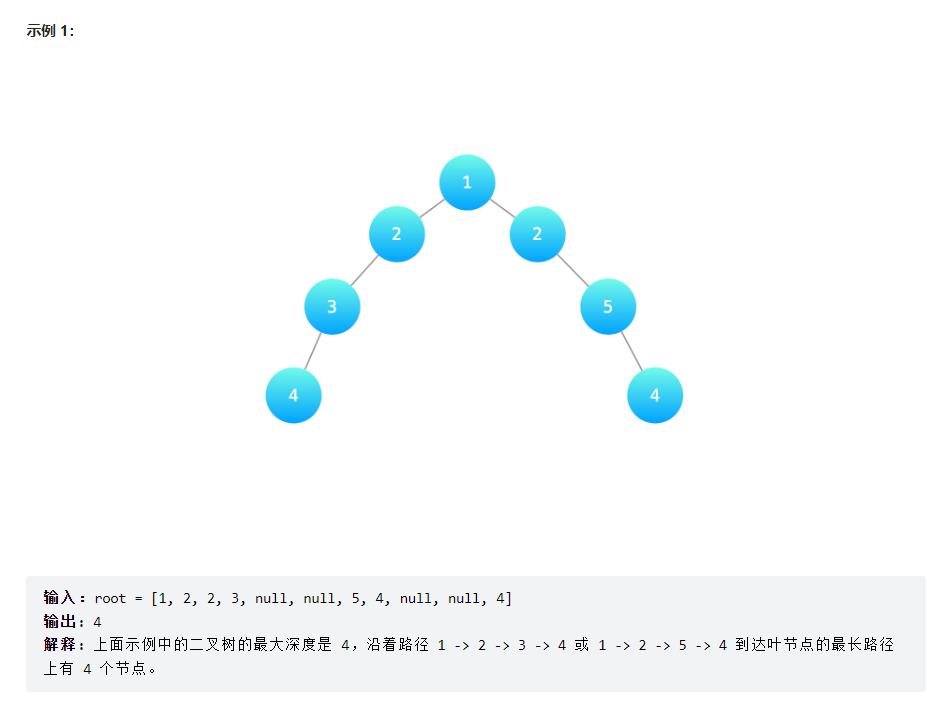
==搜索,没什么好说的==
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int maxdep = 1;
public void dfs(TreeNode root, int dep){
if(root == null) return;
dfs(root.left, dep + 1);
maxdep = Math.max(dep, maxdep);
dfs(root.right, dep + 1);
}
public int calculateDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
dfs(root, 1);
return maxdep;
}
}
判断是否为平衡二叉树
输入一棵二叉树的根节点,判断该树是不是平衡二叉树。如果某二叉树中任意节点的左右子树的深度相差不超过1,那么它就是一棵平衡二叉树。
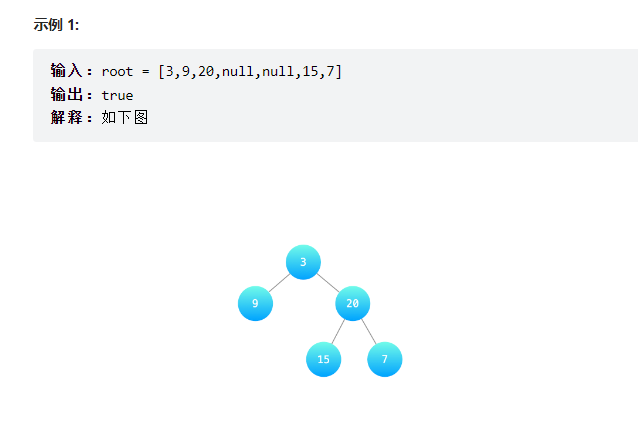
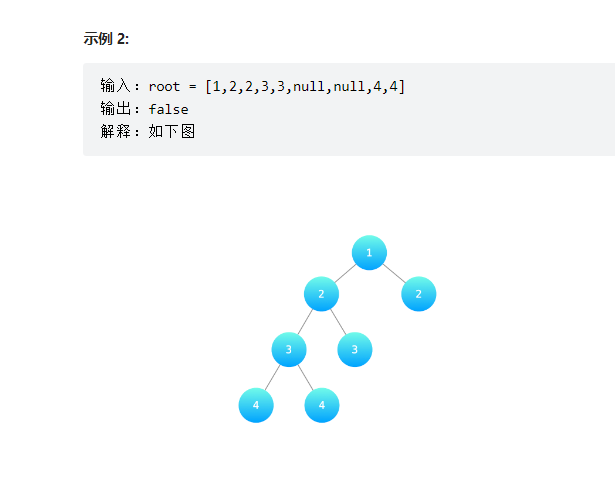
==后序遍历,往上一层一层的返回深度==
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int dep(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return 1;
int l = dep(root.left);
int r = dep(root.right);
if(l == -1 || r == -1) return -1;
if(Math.abs(l - r) > 1) return -1;
return Math.max(l, r) + 1;
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return true;
if(dep(root) == -1) return false;
return true;
}
}
==先序遍历,时间上会多出log==
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
return Math.abs(depth(root.left) - depth(root.right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
}
private int depth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(depth(root.left), depth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
作者:Krahets
链接:https://leetcode.cn/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/lx9nf7/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。